Google ADK 프레임워크 분석
Overview
Core Architecture

| Layer | Purpose | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| User Interfaces | 개발자와 최종 사용자가 ADK에 접근하고 상호작용할 수 있는 진입점(entry point)을 제공합니다. | CLI, AdkWebServer, Development Web UI |
| Core Orchestration | 에이전트 실행과 요청 처리를 관리합니다. 상위 인터페이스 계층에서 받은 명령을 실제 에이전트 실행으로 연결하는 중심 제어 역할을 합니다. | Runner, App, InvocationContext |
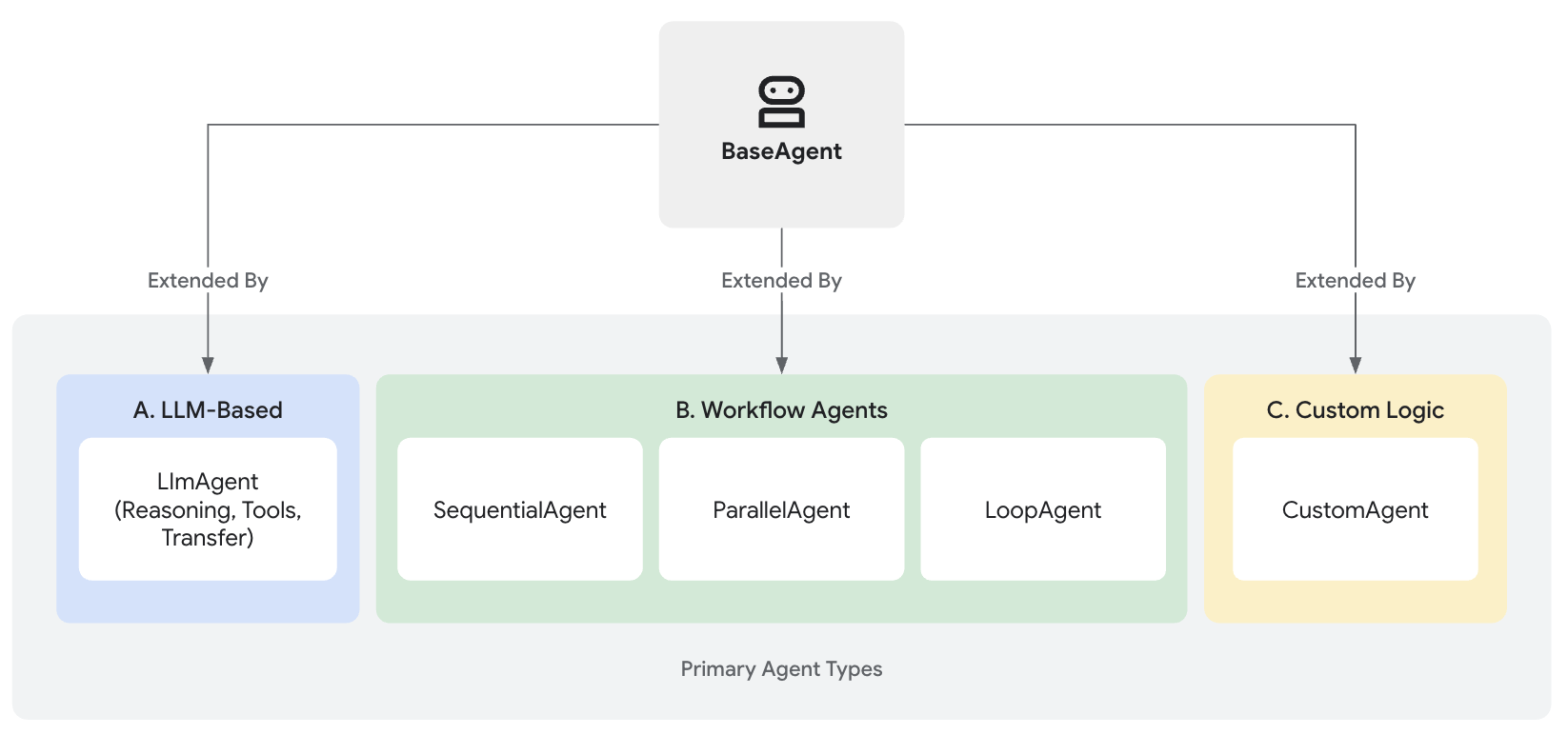
| Agent System | 다양한 에이전트 유형을 계층적으로 정의하고 구성합니다. 에이전트의 행동, 조합, 실행 방식을 담당합니다. | BaseAgent, LlmAgent, SequentialAgent, ParallelAgent, LoopAgent |
| Model Integration | 여러 LLM(대형 언어 모델)을 ADK 내에서 추상화하고 연결할 수 있도록 지원합니다. 모델 제공자별 통합을 관리합니다. | BaseLlm, Gemini, LiteLLM |
| Tool Ecosystem | 에이전트가 외부 서비스나 API를 사용할 수 있도록 하는 확장 가능한 도구 프레임워크입니다. | BaseTool, OpenAPI tools, MCP tools, Google services |
| Persistence Layer | 세션, 상태, 산출물(artifact) 등을 저장하고 관리합니다. 실행 중 생성되는 데이터를 지속적으로 보관하는 역할을 합니다. | BaseSessionService, ArtifactService, MemoryService |
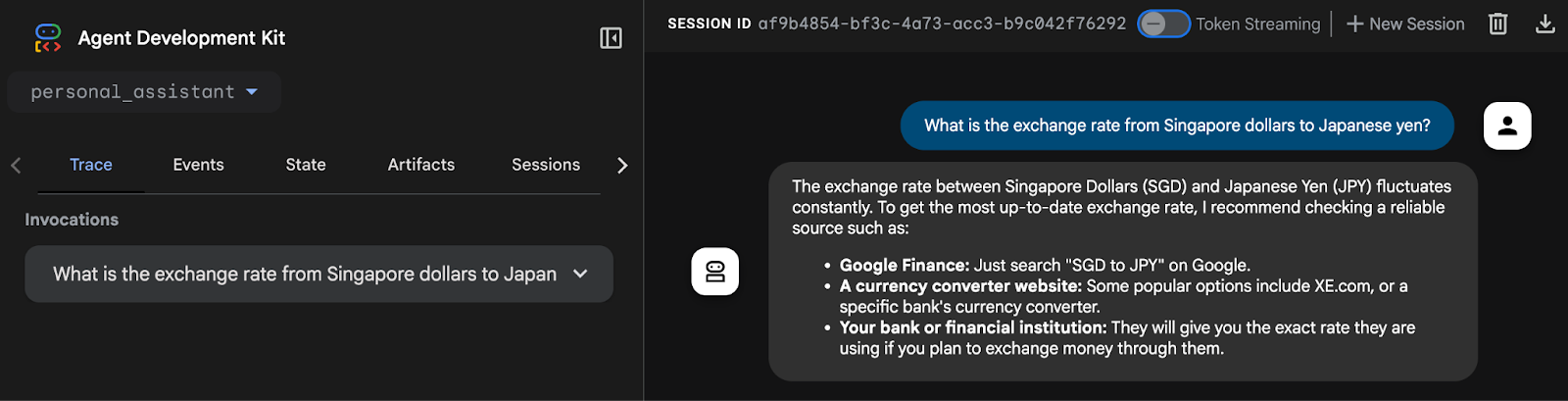
User Interfaces (사용자 인터페이스 계층)
Core Framework Components
Agent System
-
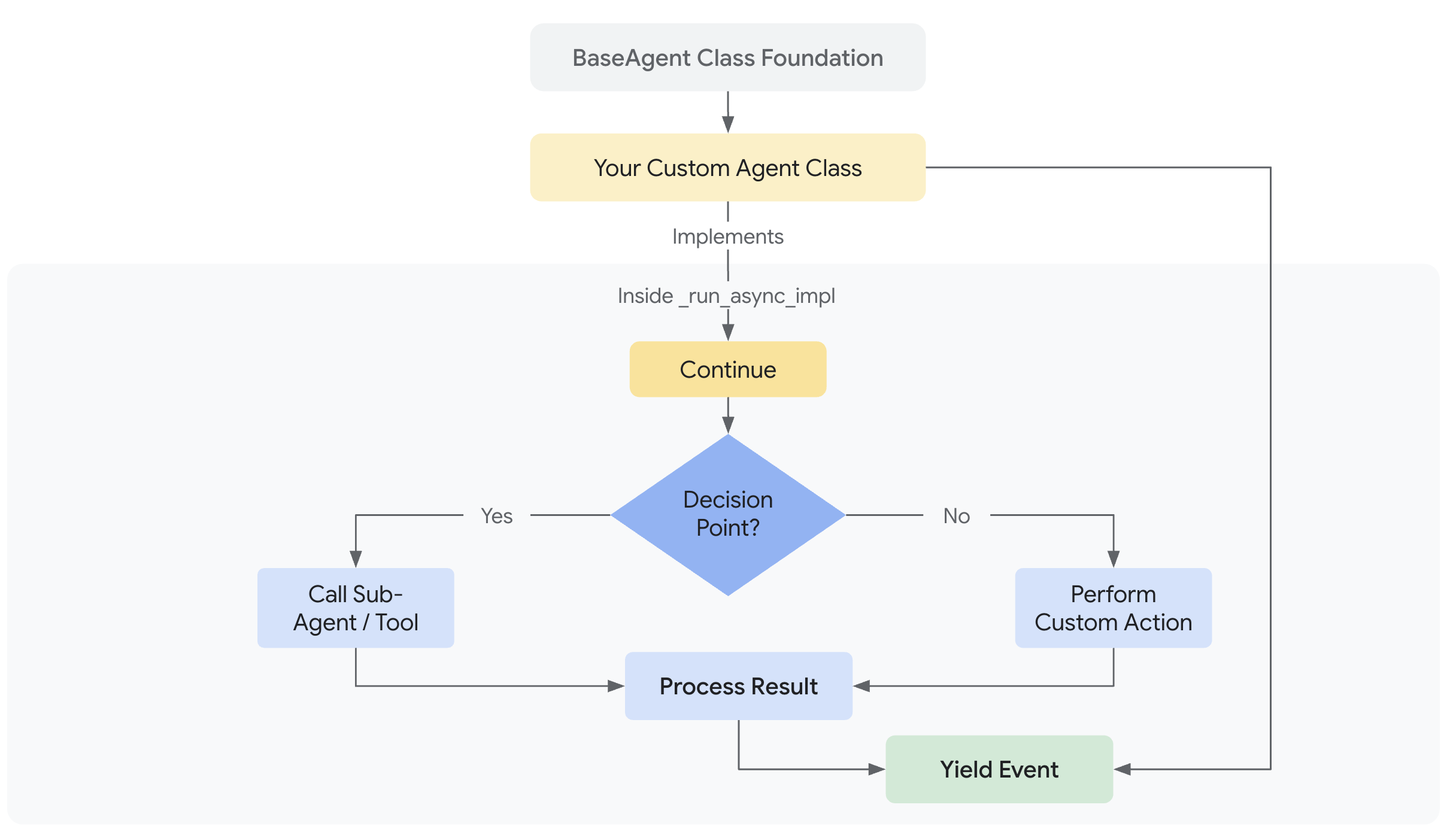
BaseAgent:
모든 에이전트의 공통 동작과 인터페이스를 정의하며, 다른 에이전트들이 이를 상속받아 구체적인 로직을 구현합니다.
-
LlmAgent:
대형 언어 모델(LLM)과 상호작용하여 추론, 응답 생성, 의사결정 등의 작업을 수행합니다.
→ 실제 작업을 수행하는 에이전트 (그 아래는 흐름만 제어)
class LlmAgent(BaseAgent): """LLM-based Agent.""" ... # Example: Defining the basic identity capital_agent = LlmAgent( model="gemini-2.0-flash", name="capital_agent", description="Answers user questions about the capital city of a given country." # instruction and tools will be added next instruction=..., tools=[] )
-
SequentialAgent:
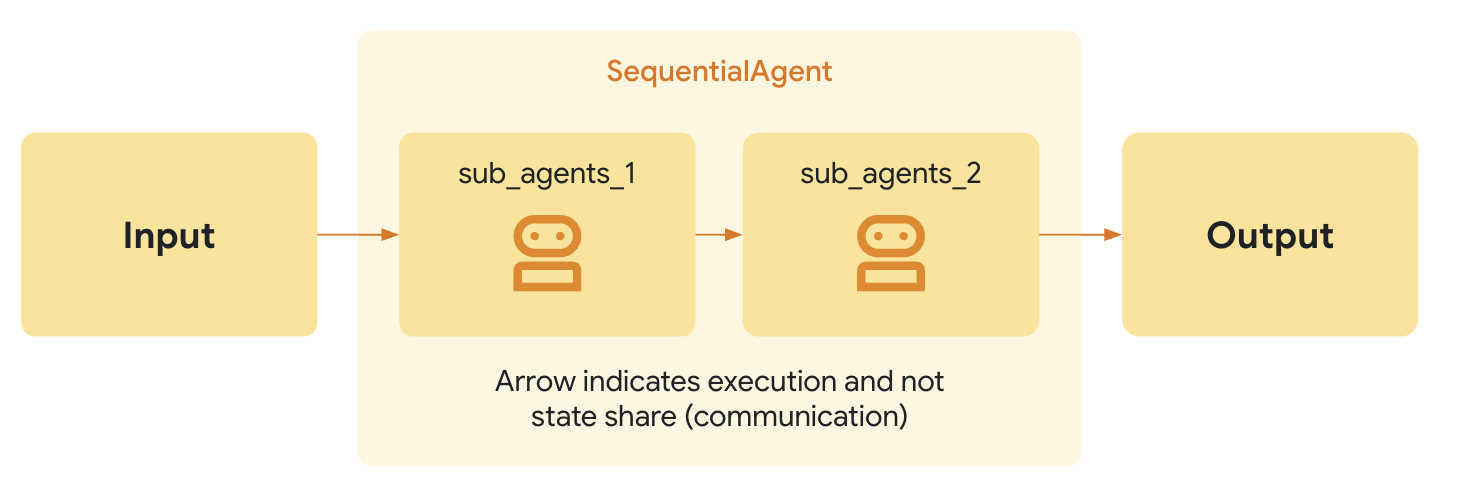
하위 에이전트(sub-agent)들을 순차적으로(Sequence) 실행하는 에이전트입니다.
한 에이전트의 출력이 다음 에이전트의 입력으로 전달되는 구조를 가집니다.
SequentialAgent(sub_agents=[CodeWriterAgent, CodeReviewerAgent, CodeRefactorerAgent])
-
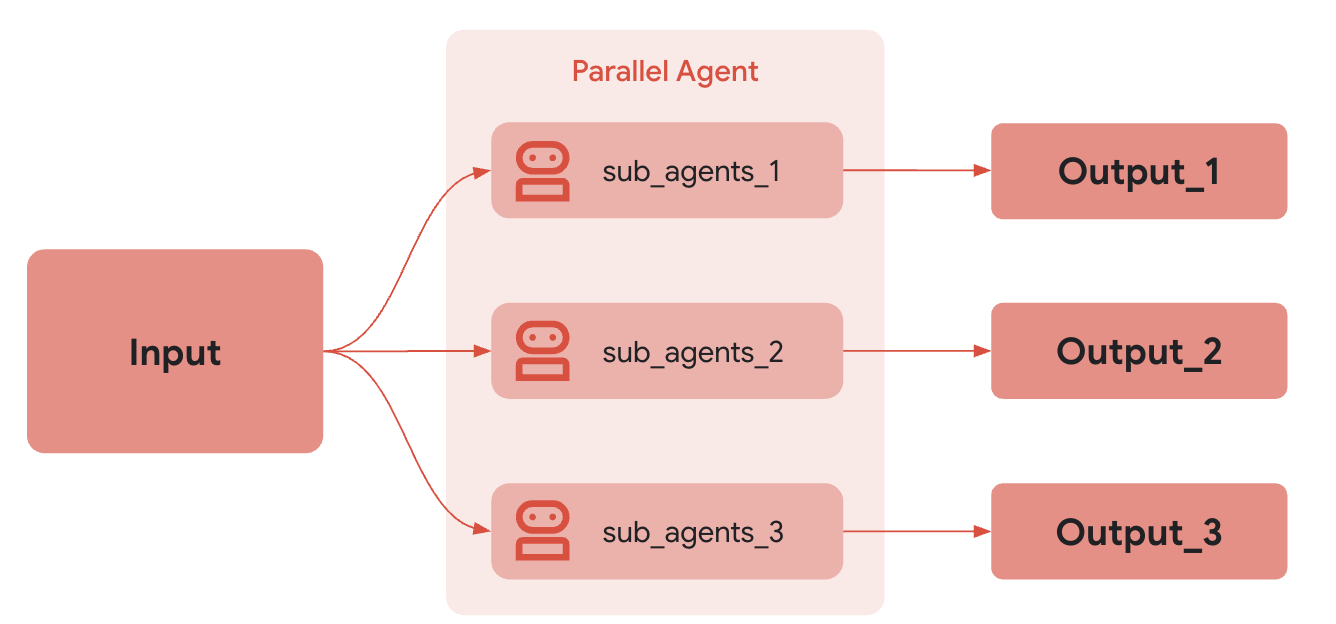
ParallelAgent:
여러 하위 에이전트들을 동시에(Concurrent) 실행하는 에이전트입니다.
병렬 실행을 통해 처리 속도를 높이거나 여러 작업을 동시에 수행할 수 있습니다.
(속도가 중요한 경우 / 의존성이 없는 작업 / 리소스 집약적인 상황에서 유리)
-
LoopAgent:
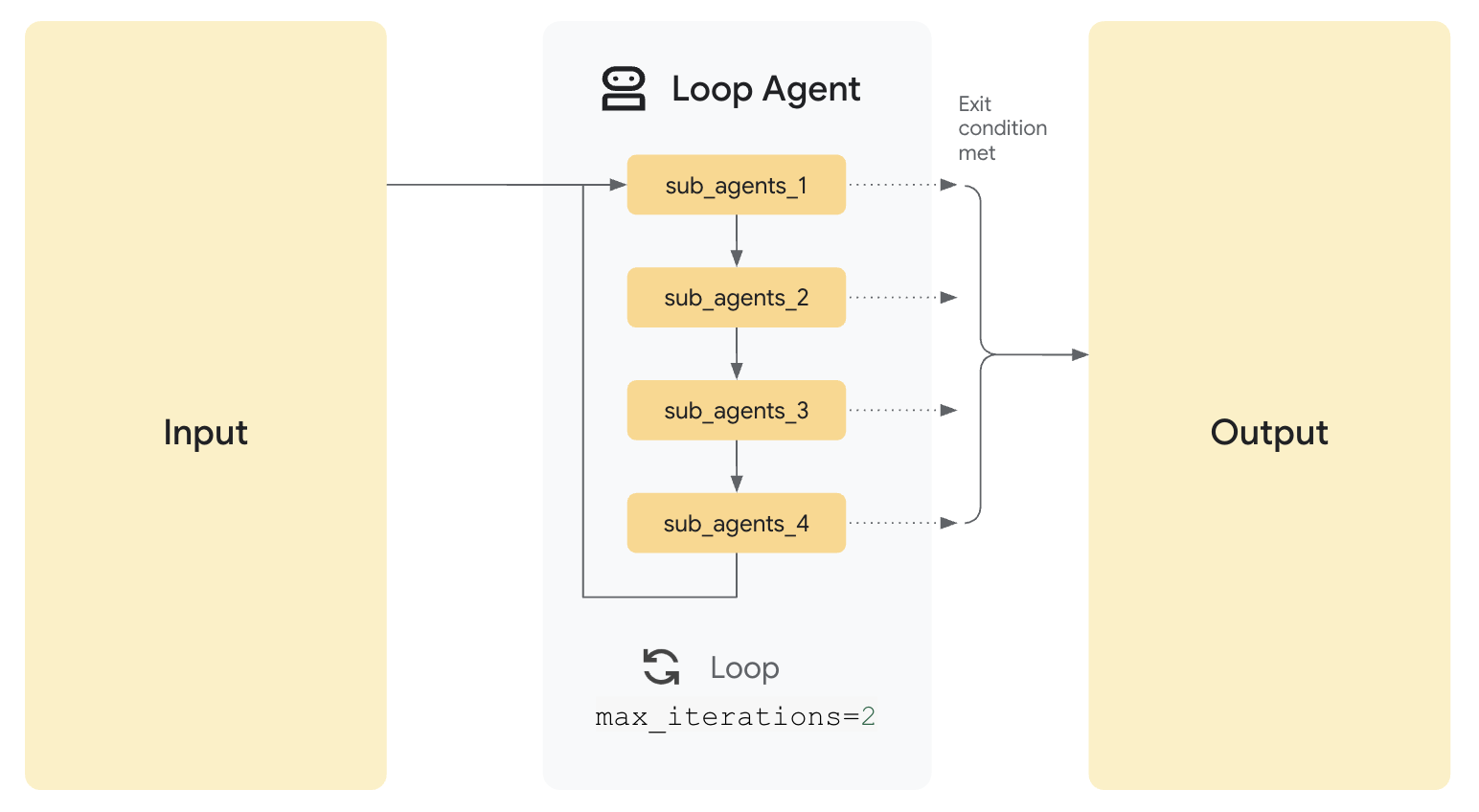
반복 실행(Iterative Execution)을 수행하는 에이전트로,
최대 반복 횟수(max iterations)를 설정하여 주어진 조건 하에서 반복적으로 실행을 제어합니다.
LoopAgent(sub_agents=[WriterAgent, CriticAgent], max_iterations=5)
CriticAgent에서 기준을 만족하면 5번 이내에 중단되는 구조
Tools를 결합하여 Agent 실행 흐름 제어하는 부분
# LlmAgent - 실제 작업 수행 (주사위 굴리기) roll_agent = LlmAgent( name="roll_agent", model="gemini-2.0-flash", # model 필드 필수 tools=[roll_die] ) # LlmAgent - 실제 작업 수행 (소수 확인) prime_agent = LlmAgent( name="prime_agent", model="gemini-2.0-flash", # model 필드 필수 tools=[check_prime] ) parallel_agent = ParalleAgent( name="prime_agent", model="gemini-2.0-flash", # model 필드 필수 tools=[check_prime] ) # SequentialAgent - 실행 흐름만 제어 root_agent = SequentialAgent( name="simple_sequential_agent", sub_agents=[roll_agent, prime_agent] # model 필드 없음 )
출력요소를 제어하는 부분 (generate_content_config / Structuring Data)
from google.genai import types agent = LlmAgent( # ... other params generate_content_config=types.GenerateContentConfig( temperature=0.2, # More deterministic output max_output_tokens=250, safety_settings=[ types.SafetySetting( category=types.HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT, threshold=types.HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE, ) ] ) )
json formating …
output format:
{"capital" : str}
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field class CapitalOutput(BaseModel): capital: str = Field(description="The capital of the country.") structured_capital_agent = LlmAgent( # ... name, model, description instruction="""You are a Capital Information Agent. Given a country, respond ONLY with a JSON object containing the capital. Format: {"capital": "capital_name"}""", output_schema=CapitalOutput, # Enforce JSON output output_key="found_capital" # Store result in state['found_capital'] # Cannot use tools=[get_capital_city] effectively here )
Models
| 구성 요소 (Component) | 역할 (Purpose) |
|---|---|
| BaseLlm | 모든 LLM 제공자를 위한 추상 인터페이스(Abstract Interface). 모델 호출, 입력 포맷팅, 응답 처리 등의 공통 기능을 정의합니다. |
| Gemini | Google Gemini 모델과의 네이티브 통합(Native Integration)을 제공합니다. 고급 기능(멀티모달 처리, 고성능 API 등)을 지원합니다. |
| LiteLLM | LiteLLM 라이브러리를 통해 100개 이상의 모델 제공자(예: OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral 등)를 단일 인터페이스로 감싸는 래퍼(Wrapper) 역할을 합니다. |
BaseLlm을 상속받아서 Gemini / LiteLLM을 만드는 구조
Tools
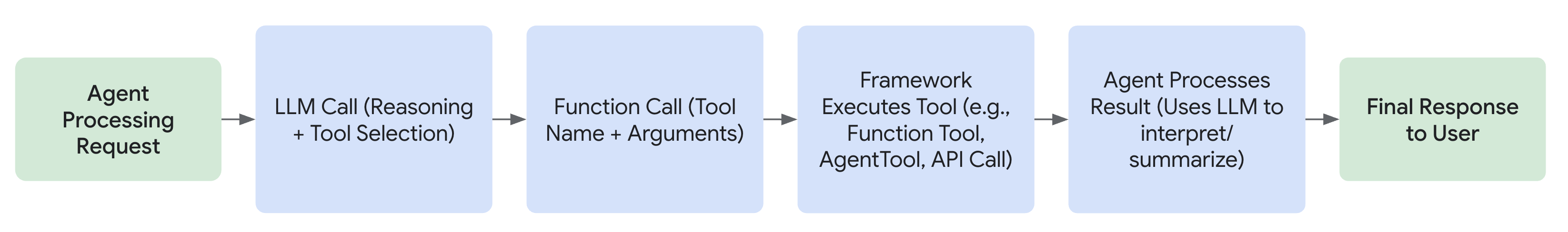
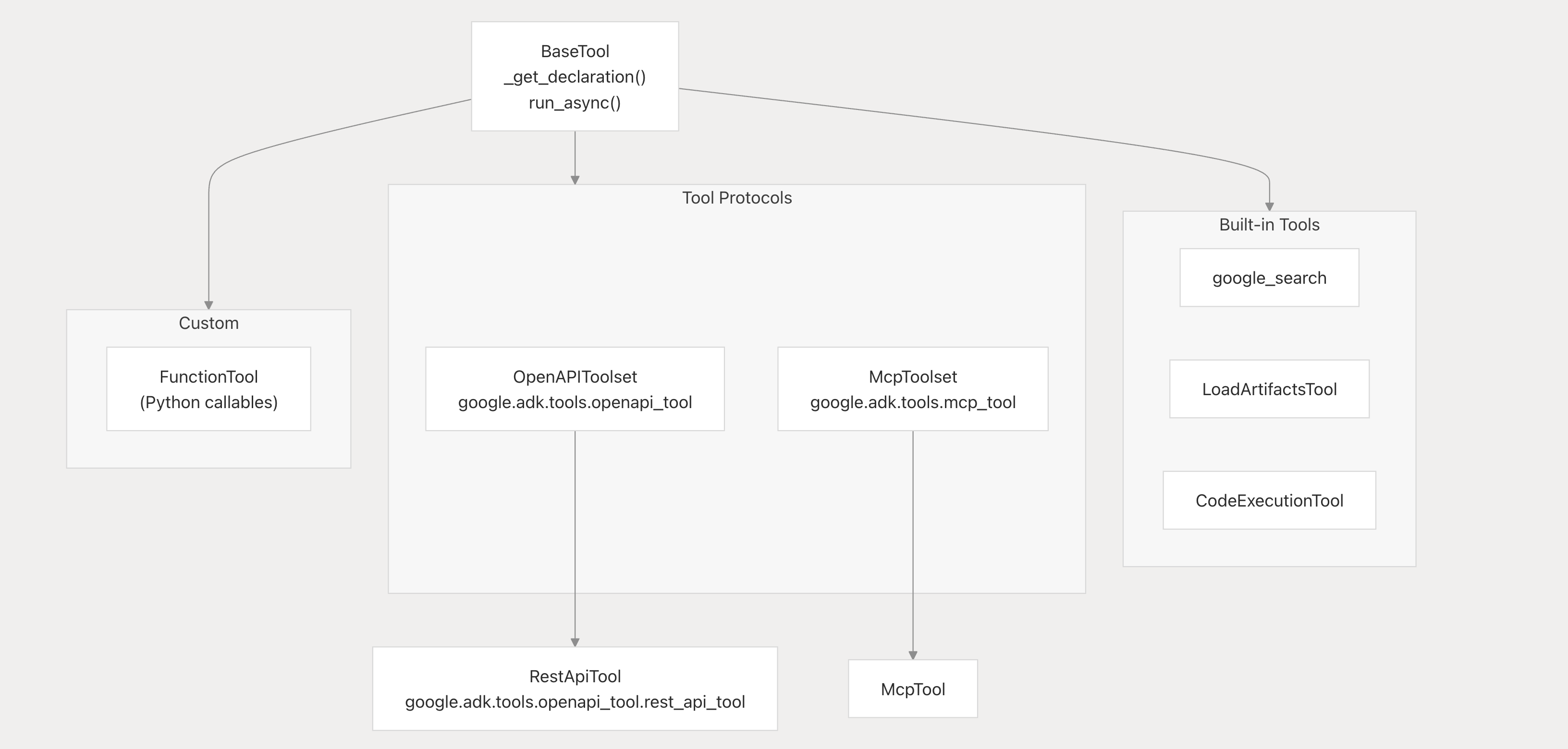
| 도구 유형 (Tool Type) | 설명 (Description) |
|---|---|
| OpenAPI Tools | OpenAPI 명세(OpenAPI Specification)로부터 도구를 자동 생성(auto-generate)합니다. 즉, REST API 명세서를 기반으로 AI 에이전트가 호출 가능한 도구를 자동으로 구성합니다. |
| MCP Tools | Model Context Protocol(MCP)을 통합하여 외부 도구 서버(external tool servers)와 연동할 수 있도록 지원합니다. 이를 통해 ADK 에이전트가 원격 도구나 서비스에 접근할 수 있습니다. |
| Function Tools | Python 함수(callable)를 도구(tool)로 감싸는(wrapper) 방식으로 구현합니다. 사용자는 간단한 Python 함수를 정의하고 이를 에이전트에서 호출 가능한 형태로 등록할 수 있습니다. |
Function Tools 예시 - 현재 시간을 가져오는 함수 / 구글 검색
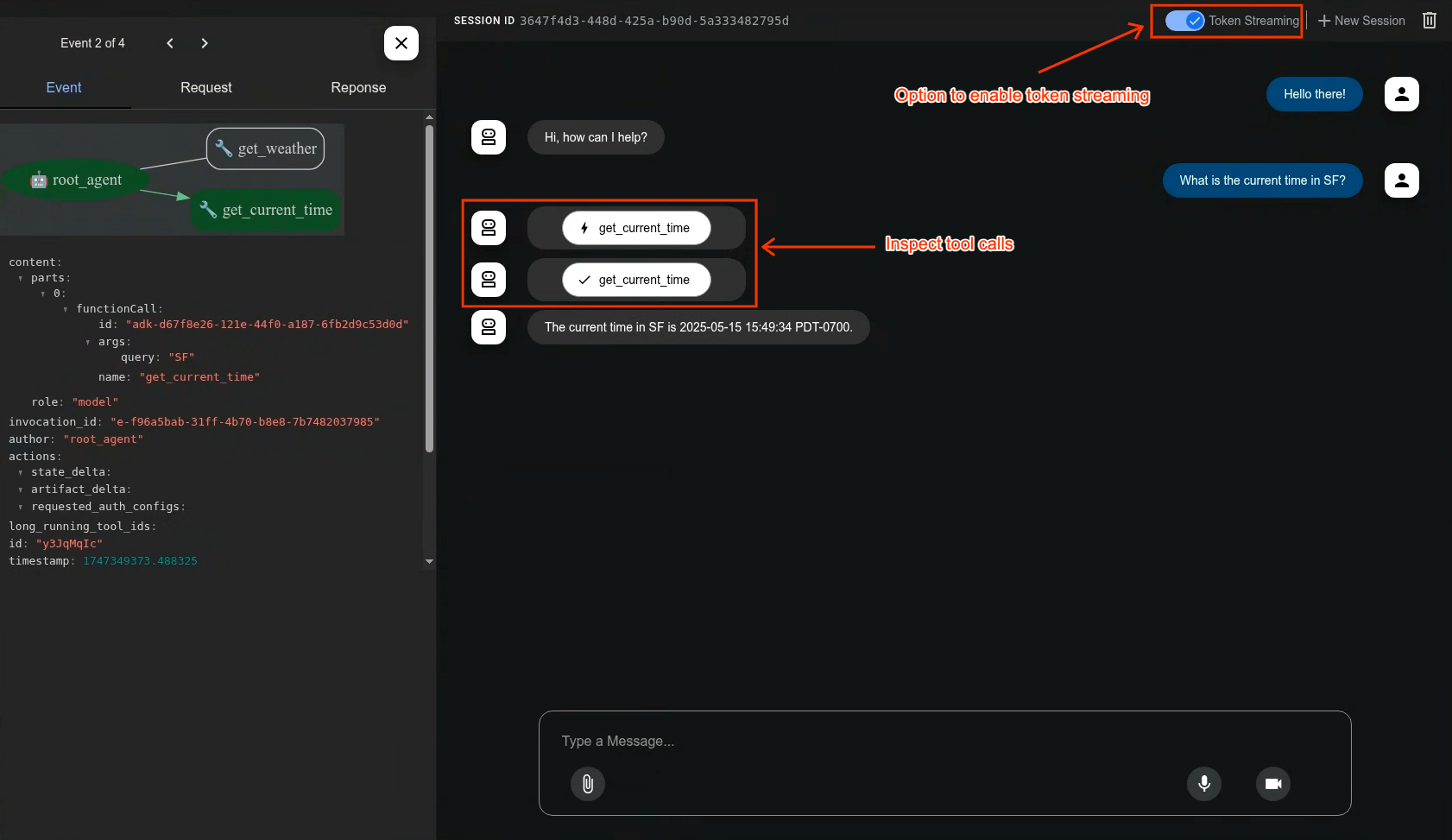
Built-in tools
from google.adk.agents import Agent from google.adk.tools import google_search # Create an agent with google search tool as a search specialist google_search_agent = Agent( model='gemini-2.5-flash', name='google_search_agent', description='A search agent that uses google search to get latest information about current events, weather, or business hours.', instruction='Use google search to answer user questions about real-time, logistical information.', tools=[google_search], )
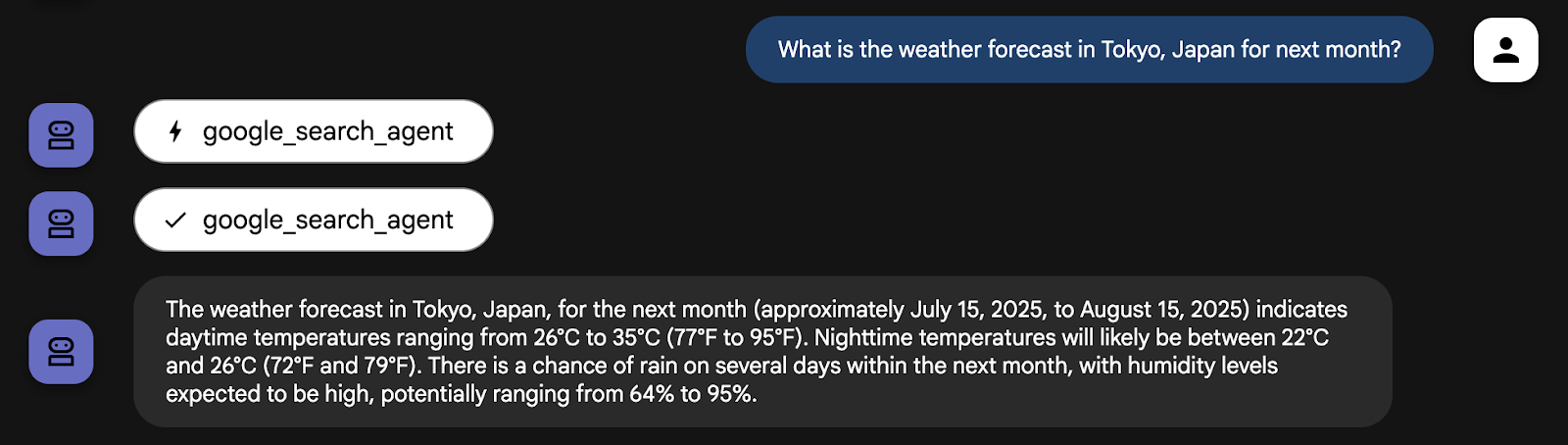
예) 다음 달 일본 도쿄의 날씨 예보는 어때?
Third Party Tools (ex. Langchain)
from langchain_community.tools import TavilySearchResults from google.adk import Agent # Instantiate the LangChain tool tavily_tool_instance = TavilySearchResults( max_results=5, search_depth="advanced", include_answer=True, include_raw_content=True, include_images=True, ) # Wrap it with LangchainTool for ADK adk_tavily_tool = LangchainTool(tool=tavily_tool_instance) # Define the ADK agent, including the wrapped tool my_agent = Agent( name="langchain_tool_agent", model="gemini-2.0-flash", description="Agent to answer questions using TavilySearch.", instruction="I can answer your questions by searching the internet. Just ask me anything!", tools=[adk_tavily_tool] # Add the wrapped tool here )
Persistence
| 서비스 (Service) | 인터페이스 (Interface) | 구현체 (Implementations) | 설명 (Description) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 세션 서비스 (Session Service) | BaseSessionService |
VertexAiSessionService, DatabaseSessionService, InMemorySessionService |
에이전트 실행 중의 세션 상태(session state)를 관리합니다. 세션 정보를 Vertex AI, 데이터베이스, 혹은 메모리에 저장할 수 있습니다. |
| 아티팩트 서비스 (Artifact Service) | ArtifactService |
GcsArtifactService, InMemoryArtifactService |
실행 과정에서 생성된 결과물(artifacts)을 저장하고 관리합니다. 예: 로그, 중간 산출물, 모델 출력 파일 등. Google Cloud Storage(GCS)나 메모리에 저장 가능. |
| 메모리 서비스 (Memory Service) | BaseMemoryService |
VertexAiMemoryService, InMemoryMemoryService |
에이전트의 기억(memory)을 관리합니다. 대화 이력, 컨텍스트, 이전 결과 등을 저장하며 Vertex AI 기반 저장소 또는 메모리를 사용합니다. |
사용 예시
- Install ADK via pip
- Create a new agent project using
adk create - Develop your agent logic in Python
- Run and test locally using
adk runoradk web - Evaluate agent performance using
adk eval - Deploy to Cloud Run, Vertex AI Agent Engine, or GKE
pip install google-adk
adk create my_agent
my_agent/ ├── __init__.py ├── agent.py ├── requirements.txt (optional) └── .env (optional)
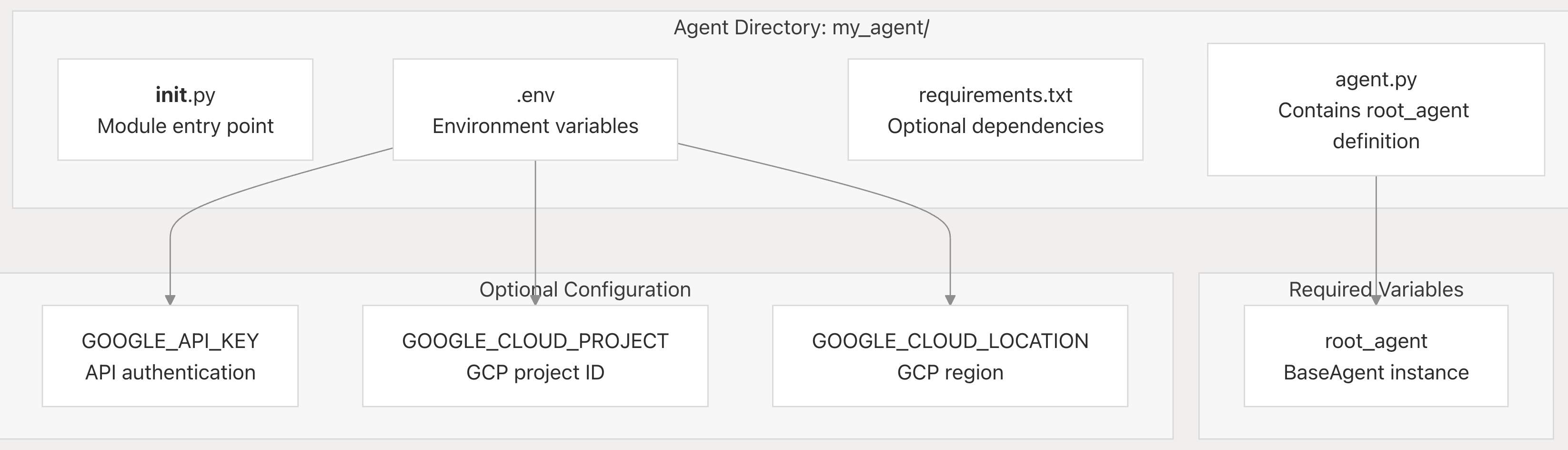
# agent.py from google.adk.agents import Agent from google.adk.tools import google_search root_agent = Agent( name="search_assistant", model="gemini-2.0-flash-exp", instruction="You are a helpful assistant. Answer user questions using Google Search when needed.", description="An assistant that can search the web.", tools=[google_search] )
adk run my_agent
딥한 개념 설명
Agent System
- Core Agent 인터페이스 (BaseAgent 중심)
- 실행 흐름 (Agent Execution Lifecycle)
- 상태 관리 (Agent State / Checkpointing)
- 콜백 시스템 (Callback Hooks)
Core Agent 인터페이스 (BaseAgent 중심)
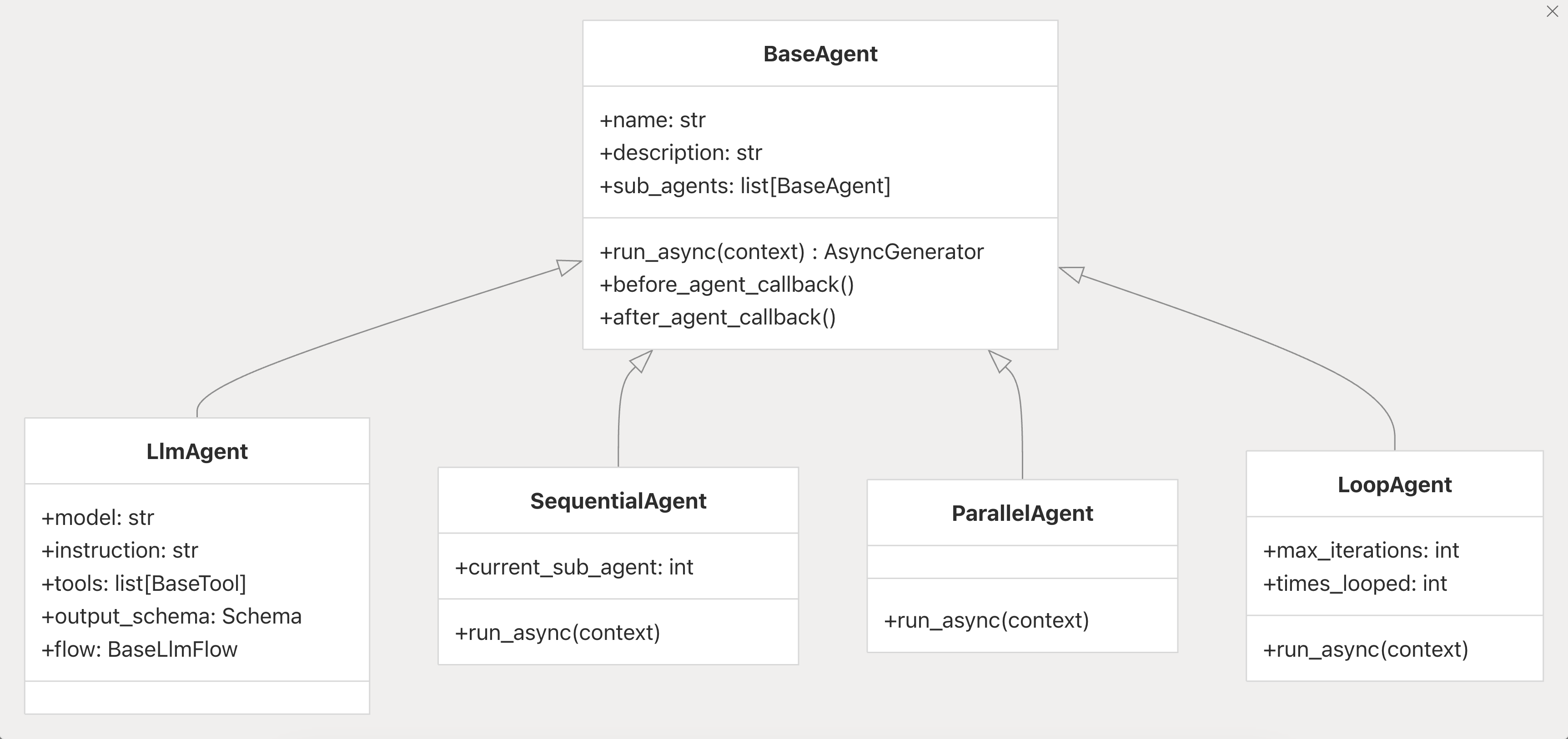
| 필드명 | 타입 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| name (str) | 문자열 | 에이전트 트리 내에서의 고유 식별자입니다. 반드시 유효한 파이썬 식별자여야 하며, "user"라는 이름은 사용할 수 없습니다. |
| description (str) | 문자열 | 상위 에이전트(parent agent)가 작업 위임(delegation) 여부를 판단할 때 사용되는 에이전트의 기능 설명입니다. |
| sub_agents (list[BaseAgent]) | 리스트 | 계층 구조 내의 하위 에이전트(sub-agent) 목록입니다. 복잡한 멀티에이전트 시스템을 구성할 때 사용됩니다. |
| parent_agent (Optional[BaseAgent]) | 선택적(BaseAgent) | 상위 에이전트에 대한 참조(reference)입니다. 초기화 시 자동으로 설정됩니다. |
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| run_async(InvocationContext) | 텍스트 기반 실행의 비동기 진입점(entry point)입니다. 실행 중 Event 객체들을 순차적으로 생성(yield) 합니다. |
| run_live(InvocationContext) | 비디오 / 오디오 기반 실시간 실행을 위한 진입점입니다. 스트리밍 또는 실시간 멀티모달 입력을 처리할 때 사용됩니다. |
| find_agent(name) | 에이전트 트리 전체에서 지정한 이름(name)을 가진 에이전트를 검색합니다. |
| find_sub_agent(name) | 현재 에이전트의 하위 계층(descendants)에서만 검색합니다. |
| clone(update) | 에이전트를 깊은 복사(deep copy)하고, 지정한 필드 값(update)을 선택적으로 수정한 새로운 인스턴스를 생성합니다. |
APi —> 답변 생성 —> 답변을 받고 동작
Execution and Orchestration
에이전트 실행 라이프사이클을 관리하고 서비스 상호 작용을 조정하며 요청 흐름을 처음부터 끝까지 오케스트레이션하는 역할 (즉, 요청 수신부터 최종 응답 반환까지의 전체 사이클을 관리하고, 그 과정에서 세션, 아티팩트, 메모리, 자격증명 등 외부 서비스와의 연동을 조율하는 부분)
- 요청 라이프사이클 관리(수신 → 처리 → 응답)
- 서비스 연동(세션/아티팩트/메모리/credential)
- 실행 상태 추적(에이전트 경계 포함)
- 이벤트 스트리밍(실시간 클라이언트 전송)
- 플러그인(전/후 훅) 통합 및 변환 처리.
Running Agents (Runtime)
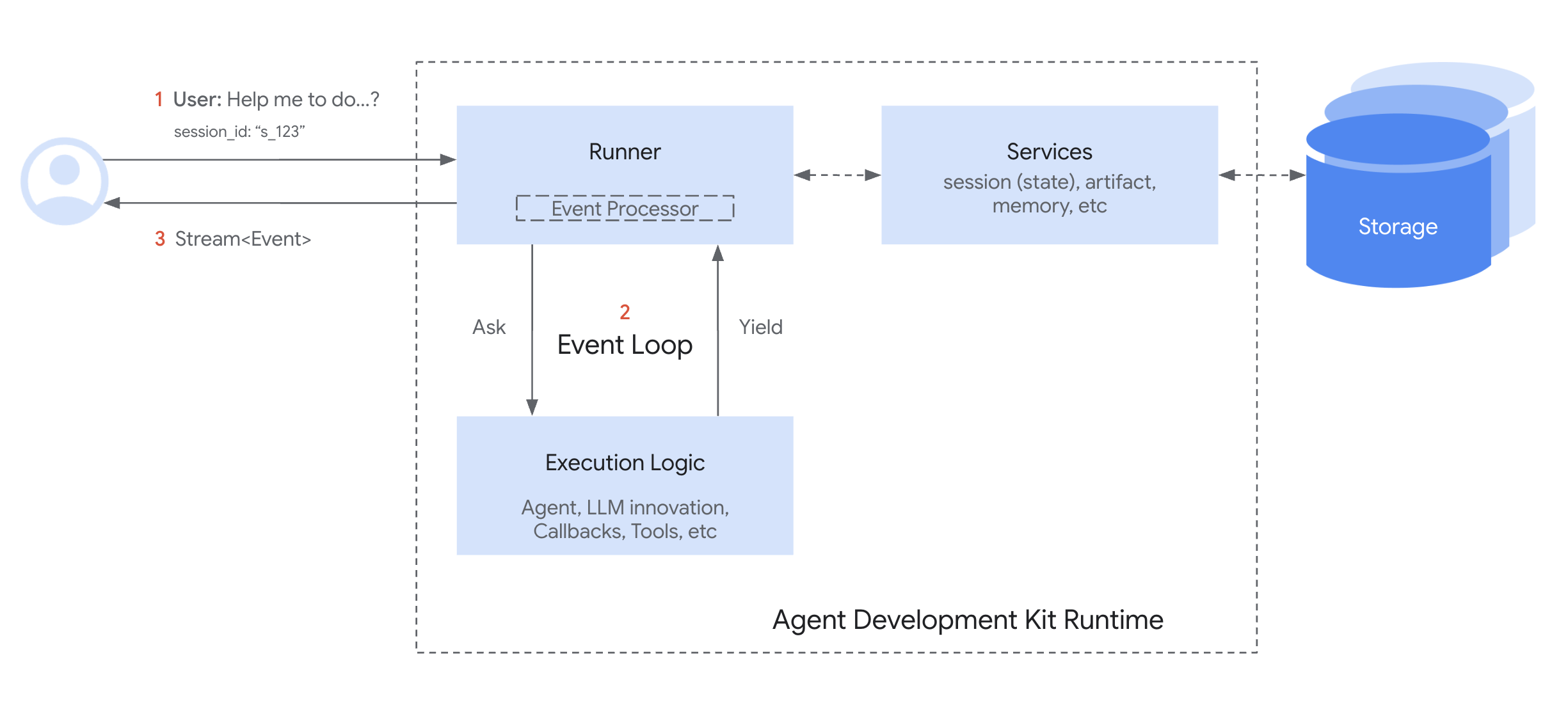
- Runner는 사용자의 질의(user query)를 받아서 메인 Agent에게 “이걸 처리해줘”라고 요청합니다.
- Agent(및 그 내부 로직)는 실행을 시작하고, 응답을 생성하거나 도구 호출(tool use) 요청, 혹은 상태 변경(state change) 같은 보고할 만한 결과가 생기면, 그 시점에서 이벤트(Event)를 발행(yield / emit)합니다.
- 이벤트 : 사용자와 에이전트 간의 대화에서 발생하는 각 메시지나 액션
- 서비스 : 에이전트가 사용하는 백엔드 기능을 제공하는 컴포넌트
- Runner는 이 이벤트를 수신하고, 그에 따라 필요한 작업(예: Service를 통해 상태 변경을 저장 등)을 처리한 후, 이벤트를 사용자 인터페이스(UI) 등 다음 단계로 전달합니다.
- Runner가 이벤트 처리를 마친 뒤에야, Agent의 로직이 다시 이어서 실행됩니다. 이때 Agent는 Runner가 반영한 변경 사항(state updates)을 인식한 상태로 이어집니다.
- 이 주기가 반복되며, Agent가 현재 질의에 대해 더 이상 새로운 이벤트를 발행하지 않을 때까지 계속됩니다.
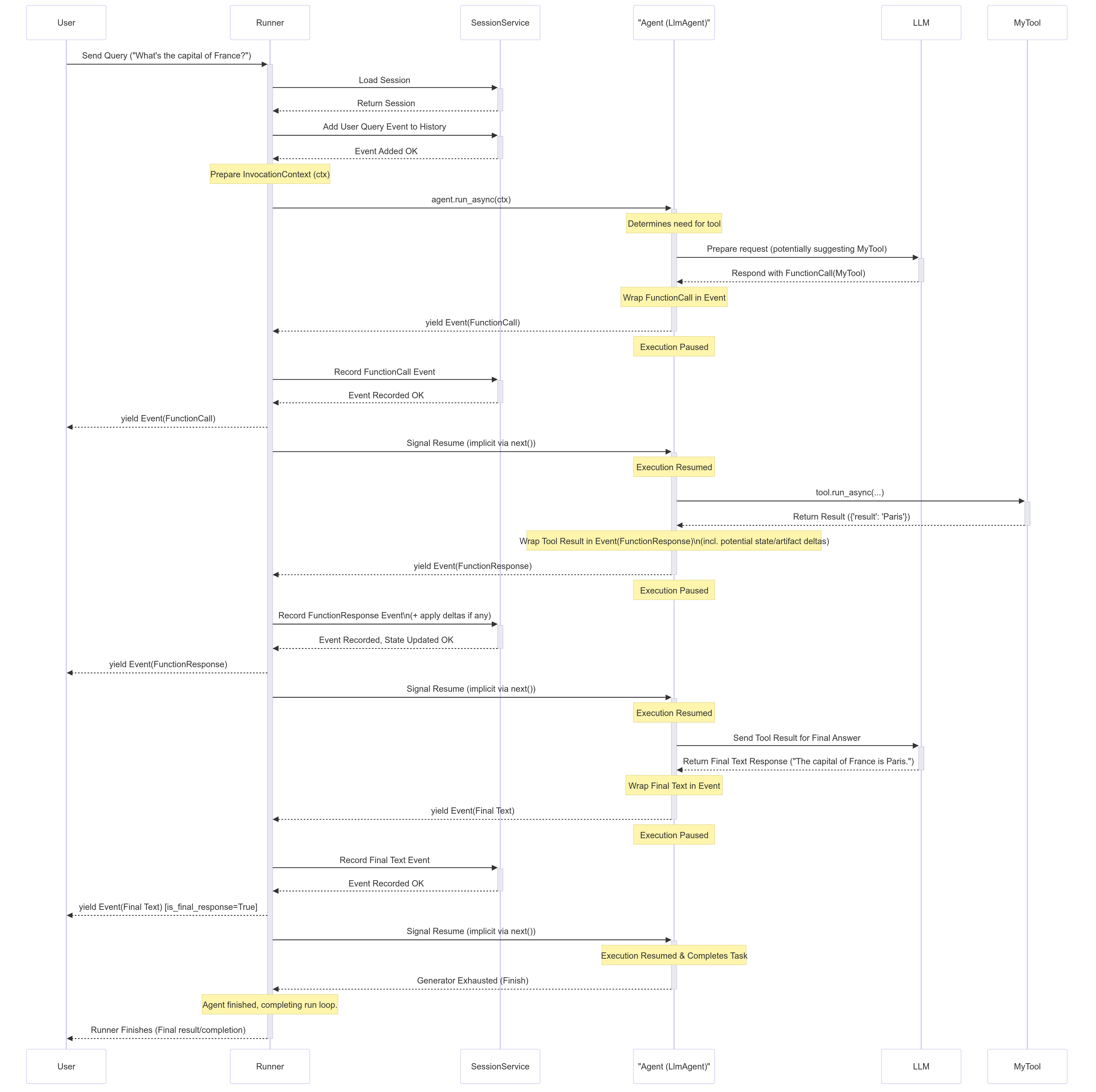
Step-by-Step Breakdown¶
- User Input: The User sends a query (e.g., "What's the capital of France?").
- Runner Starts:
Runner.run_asyncbegins. It interacts with theSessionServiceto load the relevantSessionand adds the user query as the firstEventto the session history. AnInvocationContext(ctx) is prepared. - Agent Execution: The
Runnercallsagent.run_async(ctx)on the designated root agent (e.g., anLlmAgent). - LLM Call (Example): The
Agent_Llmdetermines it needs information, perhaps by calling a tool. It prepares a request for theLLM. Let's assume the LLM decides to callMyTool. - Yield FunctionCall Event: The
Agent_Llmreceives theFunctionCallresponse from the LLM, wraps it in anEvent(author='Agent_Llm', content=Content(parts=[Part(function_call=...)])), andyieldsoremitsthis event. - Agent Pauses: The
Agent_Llm's execution pauses immediately after theyield. - Runner Processes: The
Runnerreceives the FunctionCall event. It passes it to theSessionServiceto record it in the history. TheRunnerthen yields the event upstream to theUser(or application). - Agent Resumes: The
Runnersignals that the event is processed, andAgent_Llmresumes execution. - Tool Execution: The
Agent_Llm's internal flow now proceeds to execute the requestedMyTool. It callstool.run_async(...). - Tool Returns Result:
MyToolexecutes and returns its result (e.g.,{'result': 'Paris'}). - Yield FunctionResponse Event: The agent (
Agent_Llm) wraps the tool result into anEventcontaining aFunctionResponsepart (e.g.,Event(author='Agent_Llm', content=Content(role='user', parts=[Part(function_response=...)]))). This event might also containactionsif the tool modified state (state_delta) or saved artifacts (artifact_delta). The agentyields this event. - Agent Pauses:
Agent_Llmpauses again. - Runner Processes:
Runnerreceives the FunctionResponse event. It passes it toSessionServicewhich applies anystate_delta/artifact_deltaand adds the event to history.Runneryields the event upstream. - Agent Resumes:
Agent_Llmresumes, now knowing the tool result and any state changes are committed. - Final LLM Call (Example):
Agent_Llmsends the tool result back to theLLMto generate a natural language response. - Yield Final Text Event:
Agent_Llmreceives the final text from theLLM, wraps it in anEvent(author='Agent_Llm', content=Content(parts=[Part(text=...)])), andyields it. - Agent Pauses:
Agent_Llmpauses. - Runner Processes:
Runnerreceives the final text event, passes it toSessionServicefor history, and yields it upstream to theUser. This is likely marked as theis_final_response(). - Agent Resumes & Finishes:
Agent_Llmresumes. Having completed its task for this invocation, itsrun_asyncgenerator finishes. - Runner Completes: The
Runnersees the agent's generator is exhausted and finishes its loop for this invocation.
Callback
본질적으로 콜백은 사용자가 정의하는 표준 함수입니다. 그런 다음 에이전트를 생성할 때 이 함수들을 에이전트와 연결합니다. ADK 프레임워크는 주요 단계에서 사용자의 함수를 자동으로 호출하여 관찰하거나 개입할 수 있도록 합니다. 에이전트 프로세스 중의 체크포인트와 같다고 생각하면 됩니다:
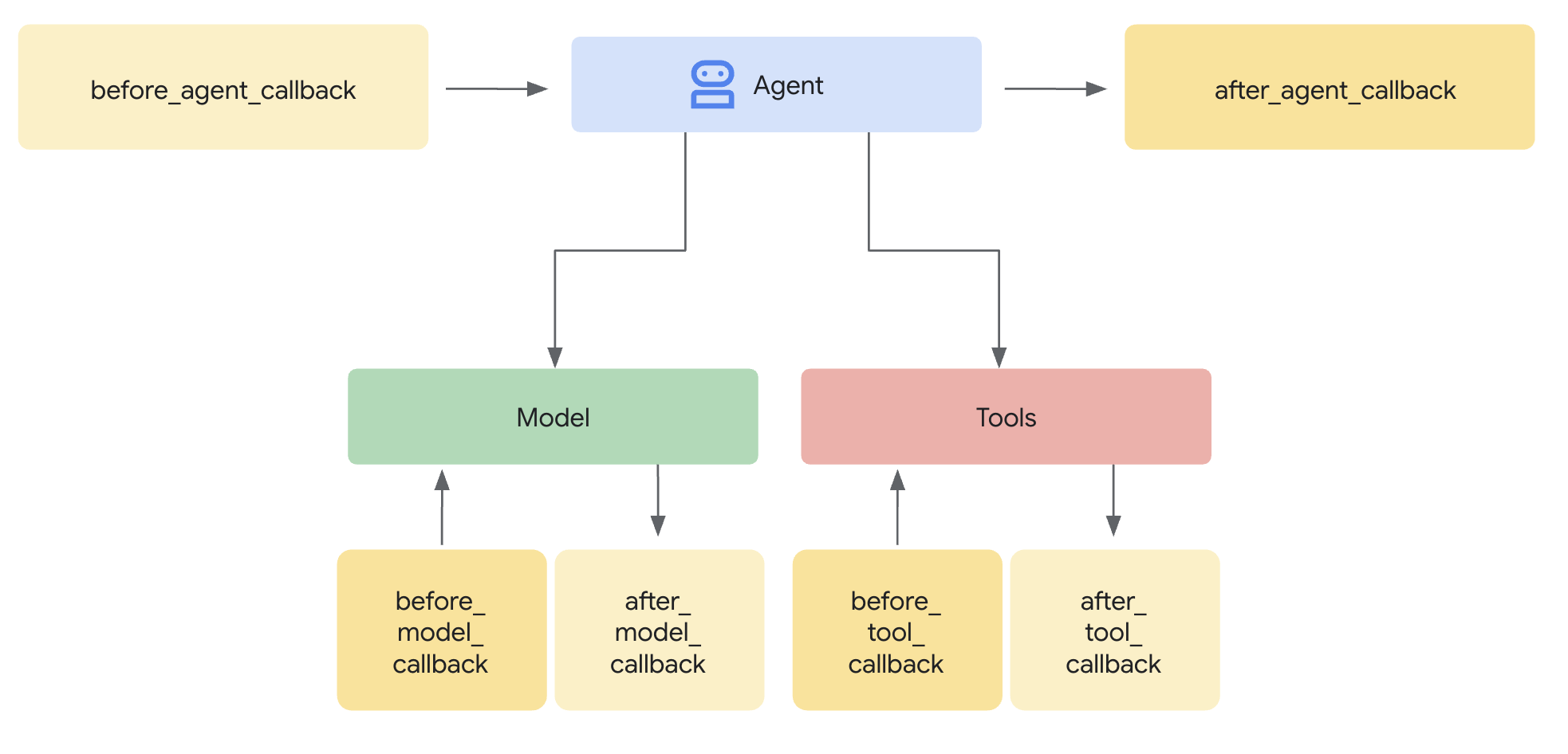
왜 사용해야 할까요?
콜백은 상당한 유연성을 제공하고 고급 에이전트 기능을 가능하게 합니다:
- 관찰 및 디버그: 모니터링 및 문제 해결을 위해 중요한 단계에서 상세한 정보를 기록합니다.
- 사용자 정의 및 제어: 에이전트를 통해 흐르는 데이터(LLM 요청이나 도구 결과 등)를 수정하거나, 로직에 따라 특정 단계를 완전히 우회할 수도 있습니다.
- 가드레일 구현: 안전 규칙을 강제하고, 입/출력을 검증하거나, 허용되지 않는 작업을 방지합니다.
- 상태 관리: 실행 중에 에이전트의 세션 상태를 읽거나 동적으로 업데이트합니다.
- 통합 및 향상: 외부 작업(API 호출, 알림)을 트리거하거나 캐싱과 같은 기능을 추가합니다.
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest from typing import Optional # --- Define your callback function --- def my_before_model_logic( callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest ) -> Optional[LlmResponse]: print(f"Callback running before model call for agent: {callback_context.agent_name}") # ... your custom logic here ... return None # Allow the model call to proceed # --- Register it during Agent creation --- my_agent = LlmAgent( name="MyCallbackAgent", model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Or your desired model instruction="Be helpful.", # Other agent parameters... before_model_callback=my_before_model_logic # Pass the function here )
참고자료
- https://google.github.io/adk-docs/
- https://github.com/google/adk-python
- https://deepwiki.com/google/adk-python/1-overview